A factory for making metal castings is known as a foundry. Metal is cast into shape by melting it into liquid, pouring the molten metal into a mold, and removing the mold material when the metal solidifies as it cools. Read More…
Precision die castings plus a multitude of related services, including engineering, designing, machining, finishing and assembly, occur at A and B Die Casting. Specializing in low to medium volume solutions, we also offer competitive prices.
Precision Die Casting since 1950. Aluminum die casting and zinc die casting for aerospace, electronic, commercial industries. Turnkey operations from design or your blue print to assembly.

Modern Aluminum Castings offers customers full-service die castings and related capabilities from design to delivery. We work with a large variety of metal options, making us your one-stop source.
At Kinetic Die Castings, we are dedicated to delivering top-tier die casting solutions that meet the diverse and demanding needs of today’s industries. Specializing in precision-engineered components, we leverage advanced die casting techniques to produce durable, lightweight parts in metals such as aluminum and zinc.

Carpenter Die Casting is more than just a die-casting manufacturer; we are your reliable partner in bringing your ideas to life. With decades of experience, a dedication to quality, and a proven track record, we stand ready to contribute our expertise to your next project. Discover the Carpenter Die Casting difference – where innovation meets tradition, and excellence is our standard.
At DyCast Specialties Corporation, we take pride in being a leading provider of top-tier die casting solutions, leveraging decades of experience and innovation to serve a wide range of industries. Our expertise lies in manufacturing precision aluminum and zinc die cast components that are renowned for their strength, durability, and intricate detailing.

More Casting Foundry Companies
What are Casting Foundries?
Usually, the metals processed are aluminum and cast iron. However, other metals, such as brass, bronze, steel, zinc, and magnesium, are also used to make castings in foundries. The components of required shapes and dimensions can be formed using this procedure.

A foundry is one of the biggest contributors to the manufacturing recycling movement, liquefying and recasting tons of scrap metals each year to make new durable products.
Many foundries utilize sand in their molding process. In addition, these foundries often utilize, recondition, and reutilize sand as another way of recycling.
The Casting Process
Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold containing a hollow cavity in the desired shape before allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified component is called a casting, which is broken out or ejected from the mold to finish the process.

Casting is most often utilized for making multifaceted shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to create by other methods.
Melting
- Virgin materials, internal and external scraps, and alloying elements are used to charge the furnace. Virgin materials refer to the commercially pure form of the main metal utilized to form a certain alloy.
- External scrap is metal from other forming procedures like punching, machining, or forging.
- Internal scrap comes from risers, gates, and faulty castings.
Degassing
- Degassing is a process that may be needed to reduce the amount of hydrogen in a batch of liquid metal. Gasses can form in metal castings in two ways:
- Physical entrapment during the casting process
- Chemical reactions in the cast material
Hydrogen is a common impurity for most cast metals.
Mold Making
- A pattern is made in the desired part’s shape. Simple designs can be made in one piece or a solid pattern.
- More complicated designs are made in two steps, called split patterns.
- The molds are made by several different procedures depending on the foundry type, metal to be poured, number of components to be produced, dimensions of the casting, and difficulty of the casting.
-
These mold processes include:
- Sand casting — Resin bonded or green sand mold
- Lost foam casting — Polystyrene pattern with a sand and ceramic mold
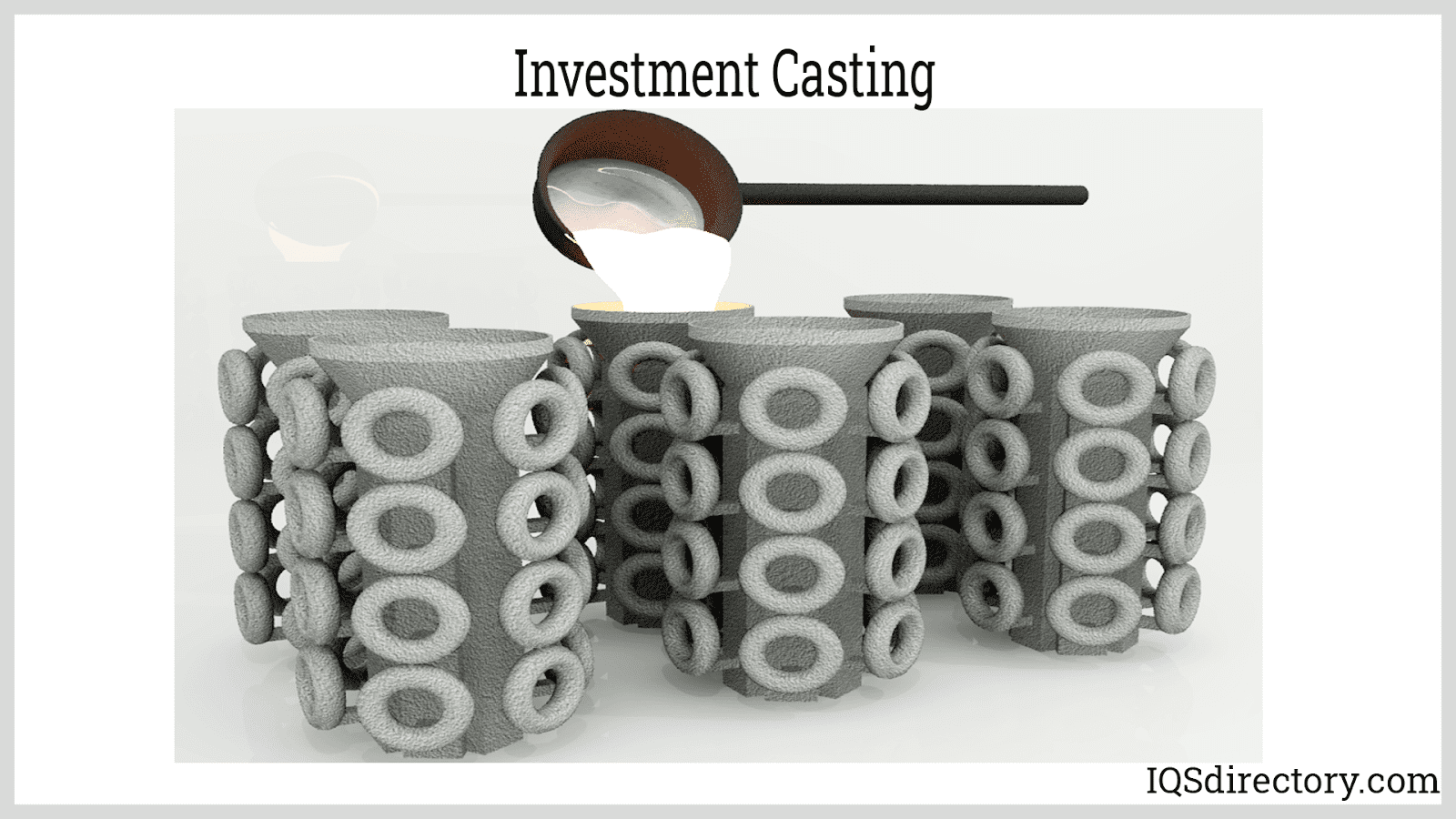
- Investment casting — Wax or alike sacrificial pattern with a ceramic mold
- Ceramic mold casting — Plaster mold
- V-process casting — Vacuum with thermoform plastic to form sand molds. No clay, moisture, or resin required
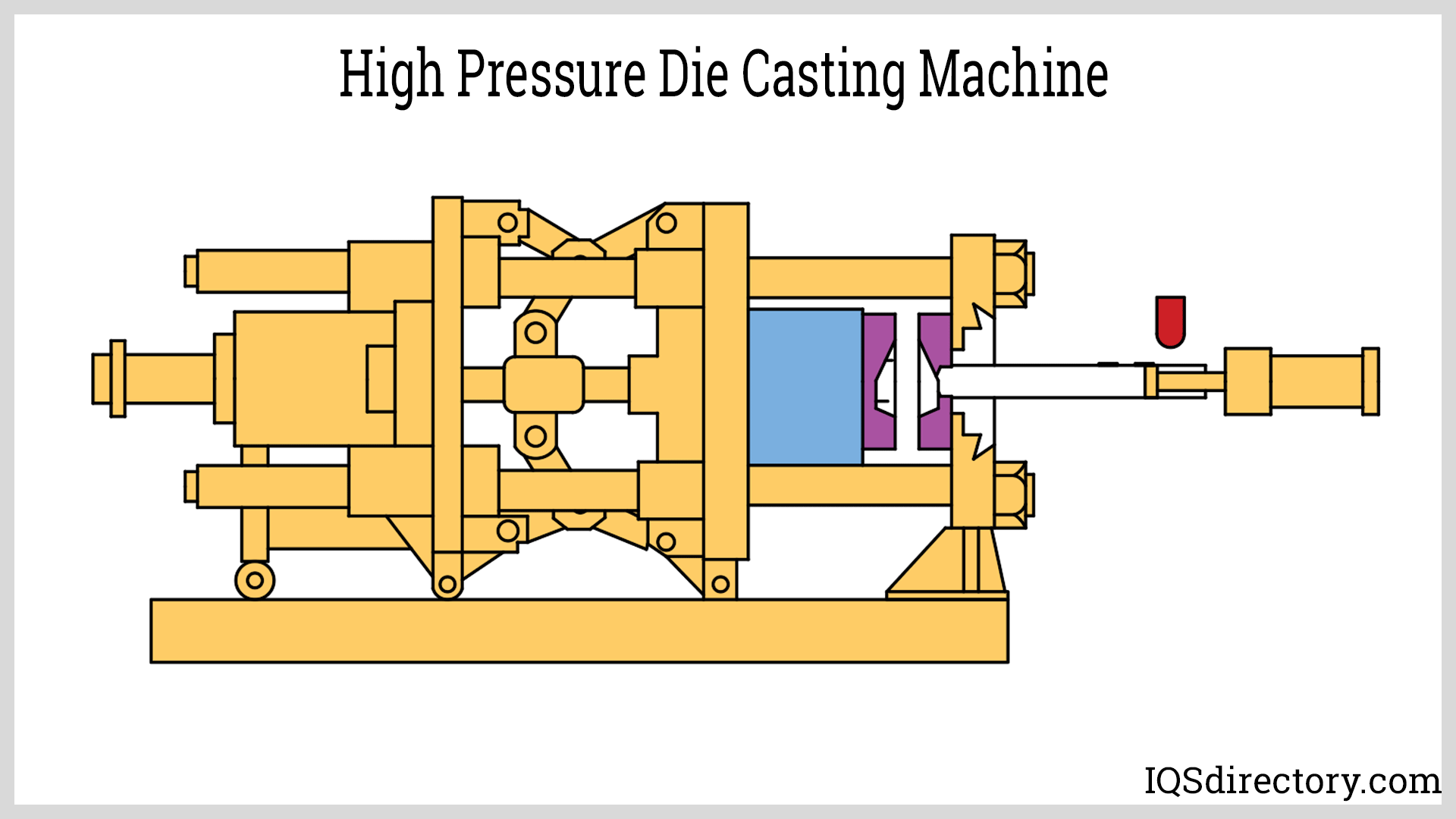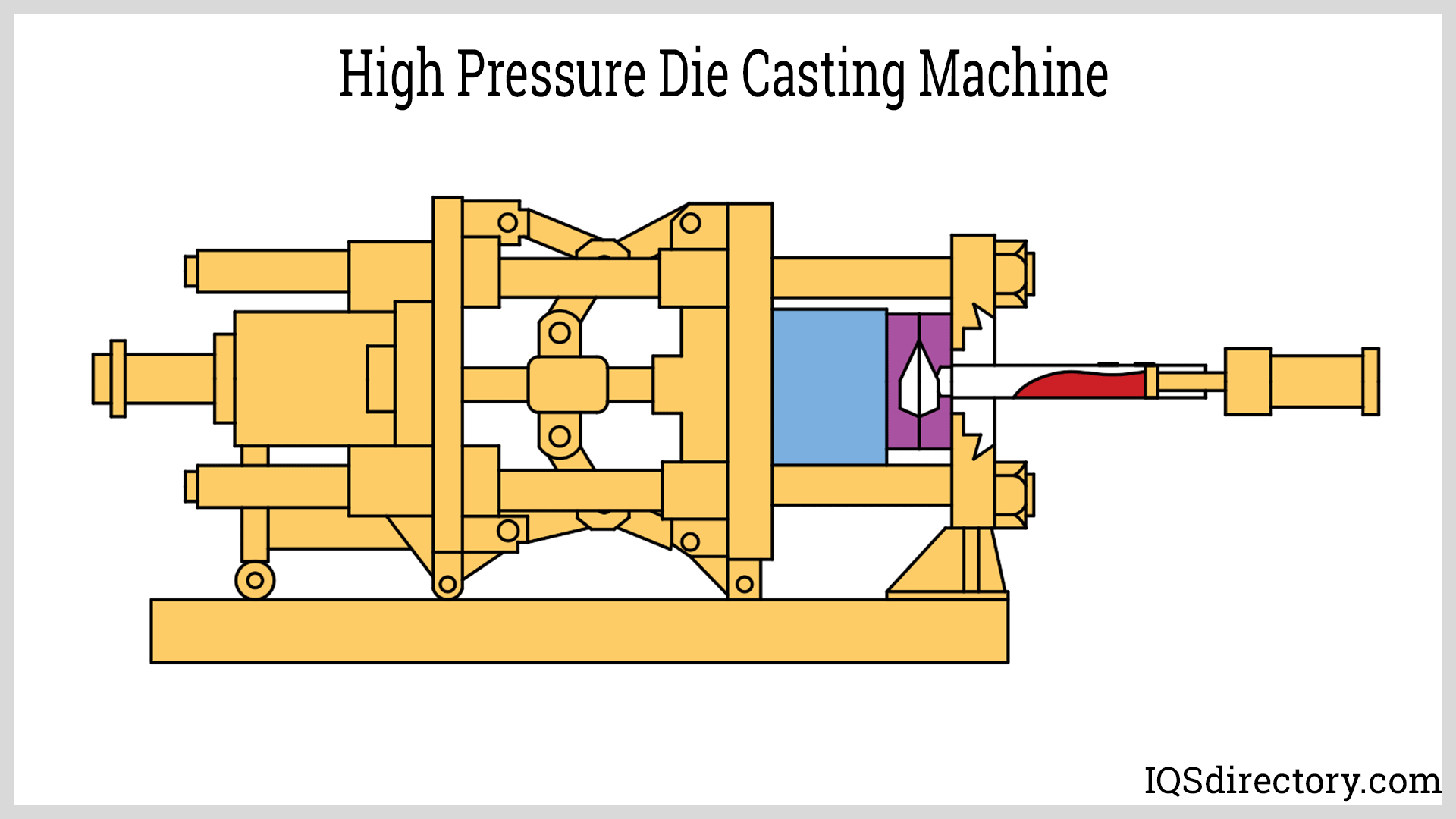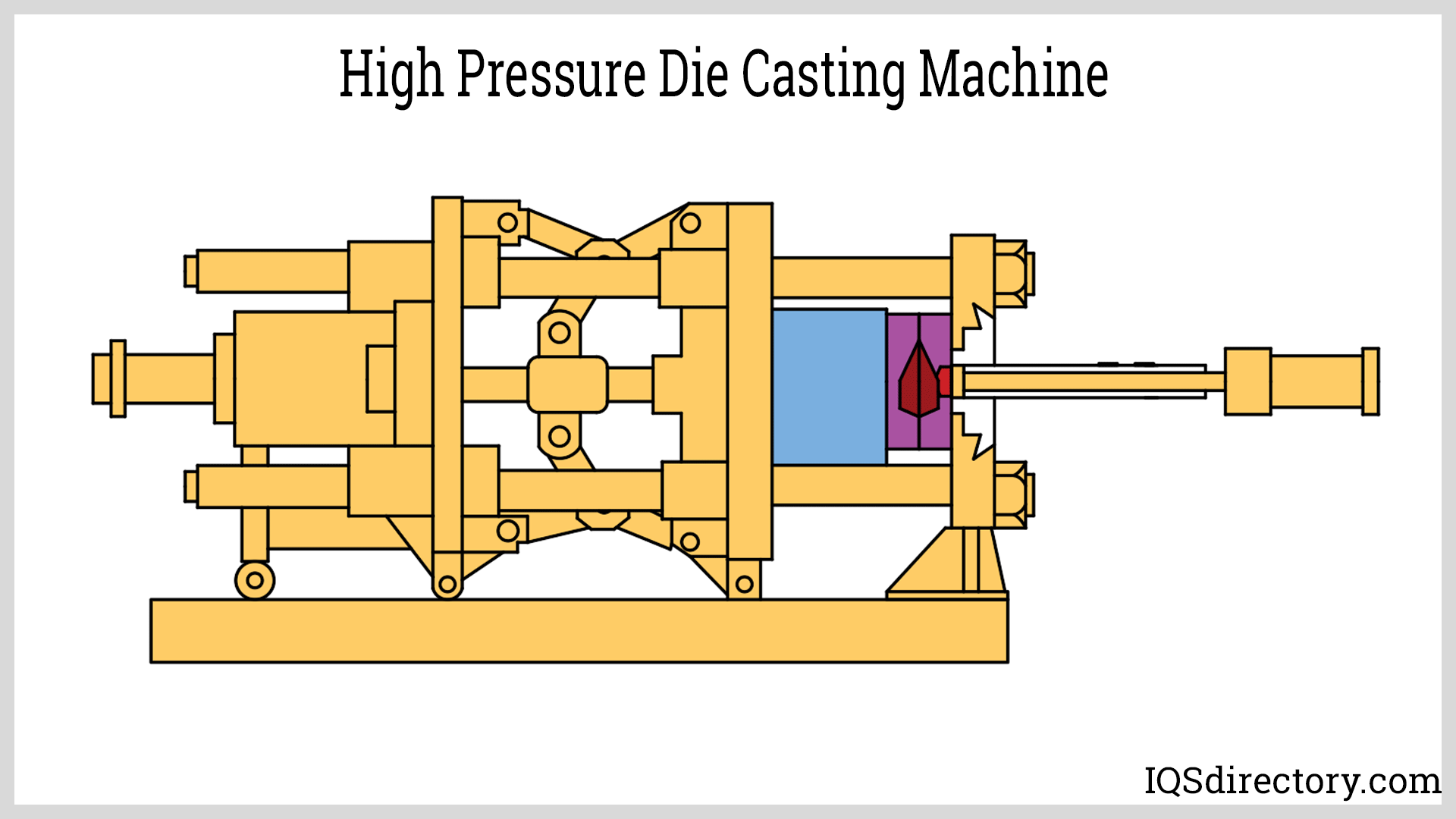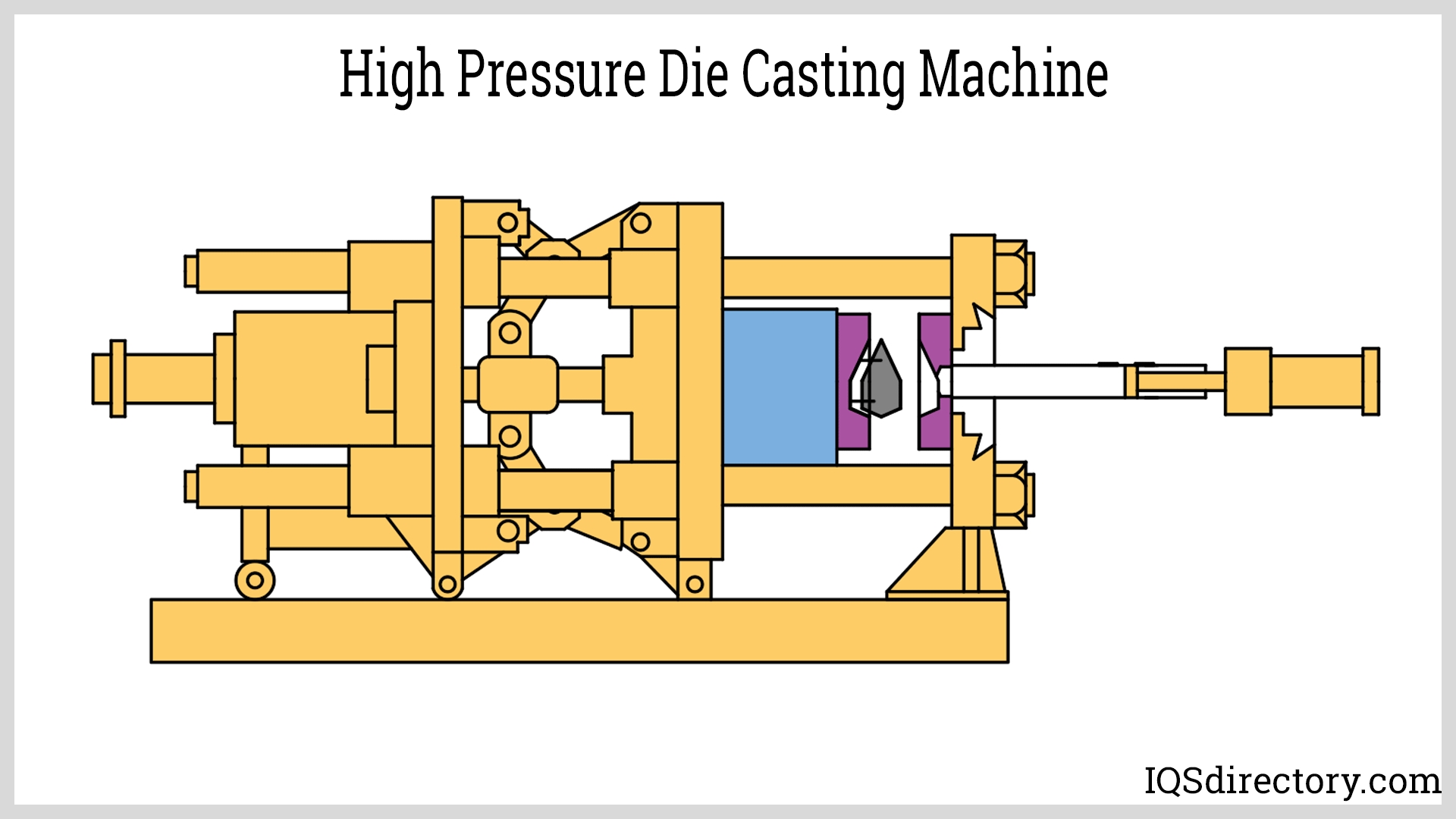
- Die casting — metal mold
- Billet casting — simple mold for producing metal ingots, usually for usage in other foundries
- Loam molding – built up mold utilized for casting huge objects
Pouring
- In a foundry, liquid metal is poured into molds.
- Pouring may be accomplished through gravity or assisted by a pressurized or vacuum gas.
- Many modern foundries utilize automatic pouring machines or robots to pour liquid metal.
Shakeout
- The solidified metal part is then removed from its mold.
- When the mold is sand-based, the part can be removed by tumbling or shaking.
- This detaches the casting from sand, which is still joined to the gates and metal runners, the passages through which the liquid metal moves to reach the part.
Degating
- Degating is the removal of the runners, heads, risers, and gates from the casting.
- Runners, risers, and gates may be removed utilizing cutting torches, ceramic cut-off blades, or band-saws.
Heat Treating
- Heat treating is a set of industrial and metalworking procedures utilized to change the physical and sometimes chemical characteristics of a metal.
Surface Cleaning
- Sand or other molding media might remain stuck to the casting.
- The surface is cleaned using a blasting process to remove any remaining mold.
Finishing
- The final stage in the casting process involves sanding, grinding, or machining the part to attain the required dimensional accuracy, physical form, and surface finish.
Foundry Design and Hazard Mitigation
A foundry is characteristically hazardous. Its primary purpose is melting metal, which commonly needs temperatures over 2597 °F (1425 °C). To give context, any water that comes in contact with an active furnace rapidly expands to 1,600 times its initial volume.
The vehement and erratic nature of chemical reactions at extremely high temperatures mandates foundry safety procedures which are equally intense. Therefore, everything about a foundry is constructed to reduce the risks associated with liquefying and transporting metal.
Foundry design tackles this by eliminating flammable material and keeping fire retardants nearby. However, due to steam explosions, water cannot be utilized to put out foundry fires. Instead, firefighting efforts focus on overwhelming the flames using industrial extinguishers and dry sand.
Foundry Equipment
Modern foundries are deeply mechanized. They contain all the machines and equipment utilized in pattern and core making, molding, and casting. That collection includes large melting furnaces, forklifts, ladles, cranes, conveyors, and transfer vessels.

The major distinction between foundries is whether they work with ferrous or non-ferrous metal. Production quantities may range from an ounce to many tons. The same variations in model and dimensions extend to pattern-making, molding machines, and many other foundry equipments.
Advantages of Casting Foundries
Following are the advantages of casting foundries:
- It is one of the most adaptable manufacturing processes.
- Castings offer uniform directional properties.
- Intricate-shaped components can be produced.
- Very complex parts may be cast in one piece.
- Production can be done using conventional foundry methods.
Disadvantages of Casting Foundries
The following are the disadvantages of casting foundries:
- It is only economical for massive production.
- The sand casting process can’t produce components in accurate sizes.
- Special casting procedures are expensive.
- Internal defects aren’t easily identified.
- Residual pores between fibers can’t be eliminated thoroughly.
Choosing the Correct Casting Foundry
For the most productive outcome when selecting a casting foundry business, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of casting foundry companies. Each casting foundry has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to communicate with the business for more information or request a quote. Review each casting foundry business website using our patented website previewer for an idea of what each casting foundry specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple casting foundries with the same form.






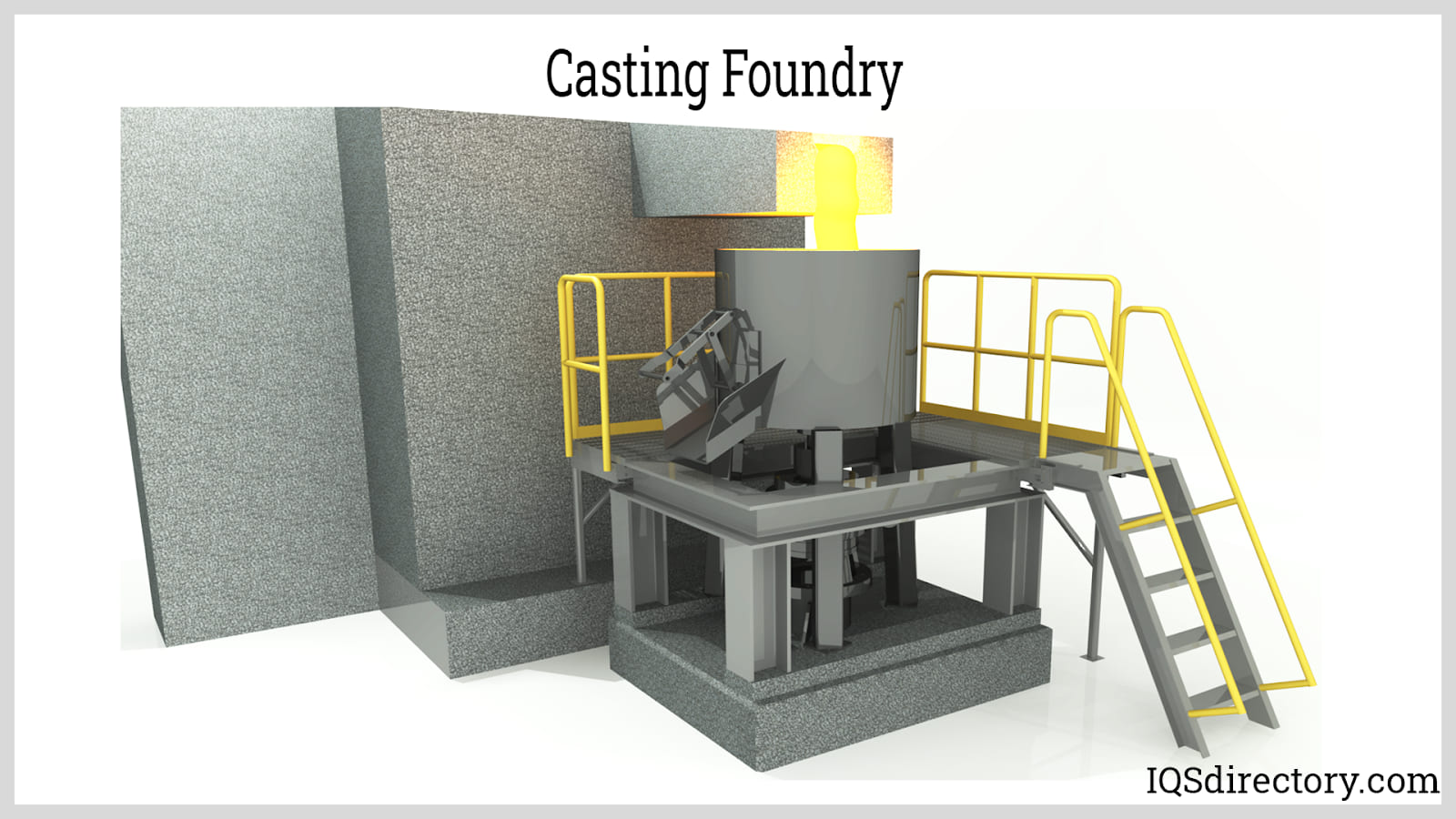
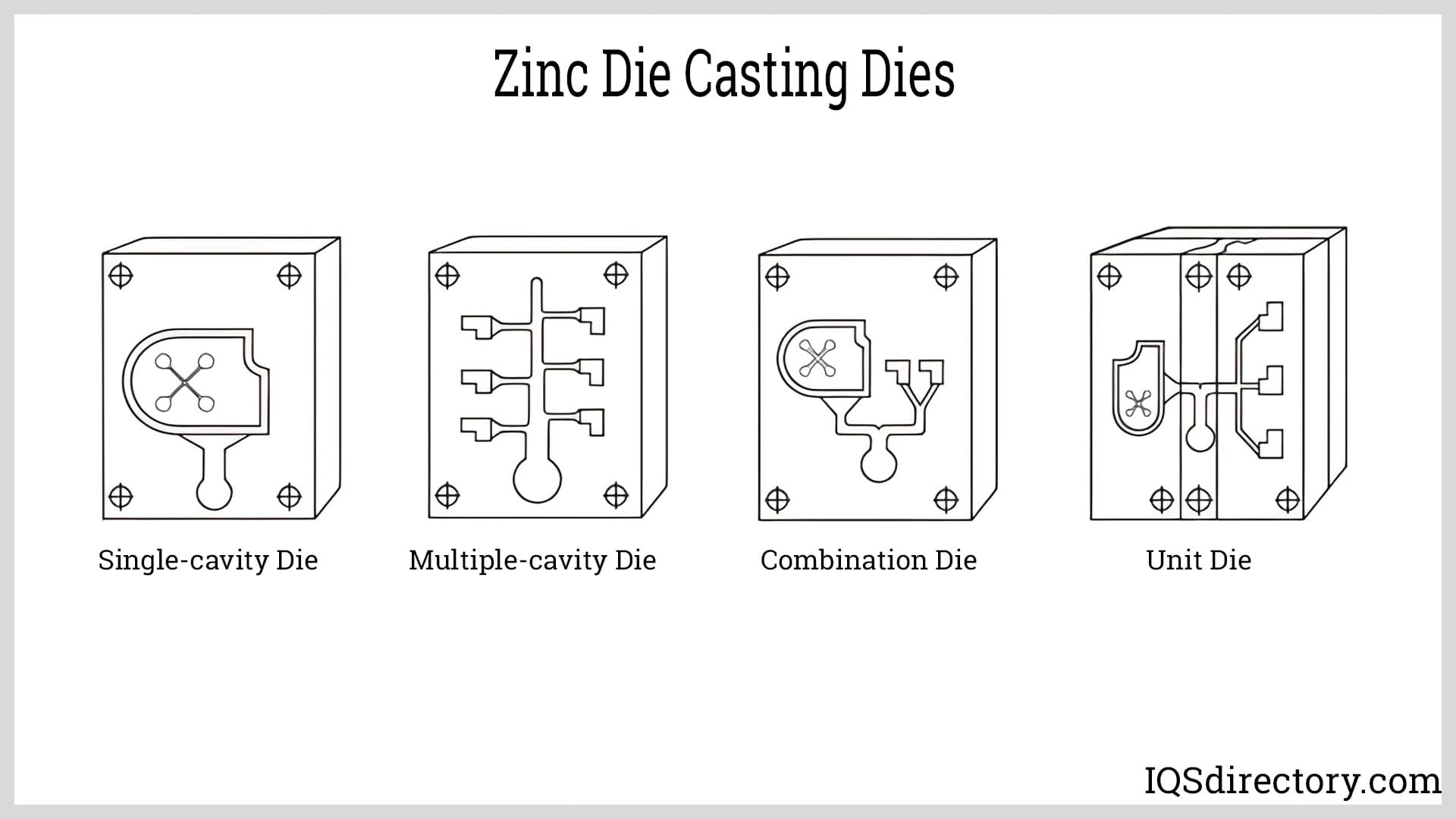


 Die Castings
Die Castings Forgings
Forgings Grey Iron Castings
Grey Iron Castings Investment Castings
Investment Castings Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services