The metal casting procedure is the earliest and most popular means of manufacturing designs in certain shapes. It is the first stage in manufacturing many products. Read More…
Precision die castings plus a multitude of related services, including engineering, designing, machining, finishing and assembly, occur at A and B Die Casting. Specializing in low to medium volume solutions, we also offer competitive prices.
Precision Die Casting since 1950. Aluminum die casting and zinc die casting for aerospace, electronic, commercial industries. Turnkey operations from design or your blue print to assembly.

Modern Aluminum Castings offers customers full-service die castings and related capabilities from design to delivery. We work with a large variety of metal options, making us your one-stop source.
At Kinetic Die Castings, we are dedicated to delivering top-tier die casting solutions that meet the diverse and demanding needs of today’s industries. Specializing in precision-engineered components, we leverage advanced die casting techniques to produce durable, lightweight parts in metals such as aluminum and zinc.

Carpenter Die Casting is more than just a die-casting manufacturer; we are your reliable partner in bringing your ideas to life. With decades of experience, a dedication to quality, and a proven track record, we stand ready to contribute our expertise to your next project. Discover the Carpenter Die Casting difference – where innovation meets tradition, and excellence is our standard.
At DyCast Specialties Corporation, we take pride in being a leading provider of top-tier die casting solutions, leveraging decades of experience and innovation to serve a wide range of industries. Our expertise lies in manufacturing precision aluminum and zinc die cast components that are renowned for their strength, durability, and intricate detailing.

More Metal Casting Companies
What are Metal Castings?
Metal castings are components formed by pouring molten metal into a mold, where the liquid metal solidifies into the desired shape. This versatile manufacturing process enables the production of parts and products from virtually any meltable metal, including aluminum, iron, steel, brass, bronze, magnesium, zinc, and copper alloys. Metal casting is the foundation of countless industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, energy, electronics, and heavy machinery manufacturing.

The ability to create intricate shapes, complex internal cavities, thin walls, and hollow sections makes metal casting ideal for producing geometries that would be challenging, expensive, or impossible to machine using subtractive manufacturing methods. Whether you require a small precision part weighing a few grams or a massive structural component weighing several tons, the metal casting process accommodates a vast range of sizes and designs. This flexibility is one reason metal castings are essential in manufacturing high-value industrial components, custom metal parts, and mass-produced consumer goods.
Why is metal casting important in modern manufacturing? Metal castings enable design freedom and cost-effective production for both prototypes and high-volume runs. They are essential for parts that demand durability, strength, or unique alloy properties. Metal casting also supports sustainability by allowing for efficient material use and recycling of scrap metal into new castings.
Understanding the Metal Casting Process: Stages and Workflows
Metal casting involves a series of carefully controlled steps. Each stage is crucial to ensuring the final product meets strict performance, durability, and dimensional accuracy standards. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main processes involved in producing a high-quality metal casting:
1. Pattern Making
- Patterns are created based on the technical drawing of the desired casting, developed during the design and planning stage.
- The choice of pattern material (such as wood, plastic, or metal) depends on the required production volume, casting complexity, and surface finish.
- Precision in pattern making is vital, as it directly affects the dimensions and quality of the final cast product.
- Advanced pattern making may use CAD/CAM software and CNC machining for repeatable accuracy and design optimization.
2. Molding and Core Making
- Patterns are transferred to the molding department, where molds are formed from sand, ceramic, or other refractory materials. The mold cavity mirrors the desired component’s shape.
- For hollow or internal features, cores are produced using core boxes and inserted into the mold. Both molds and cores are often baked for added strength before assembly.
- Proper mold and gating system design are essential to optimize the flow of molten metal, minimize defects, and ensure dimensional accuracy in the finished casting.
- Modern molding techniques include green sand molding, chemically bonded sand, shell molding, and even 3D-printed molds for rapid prototyping.
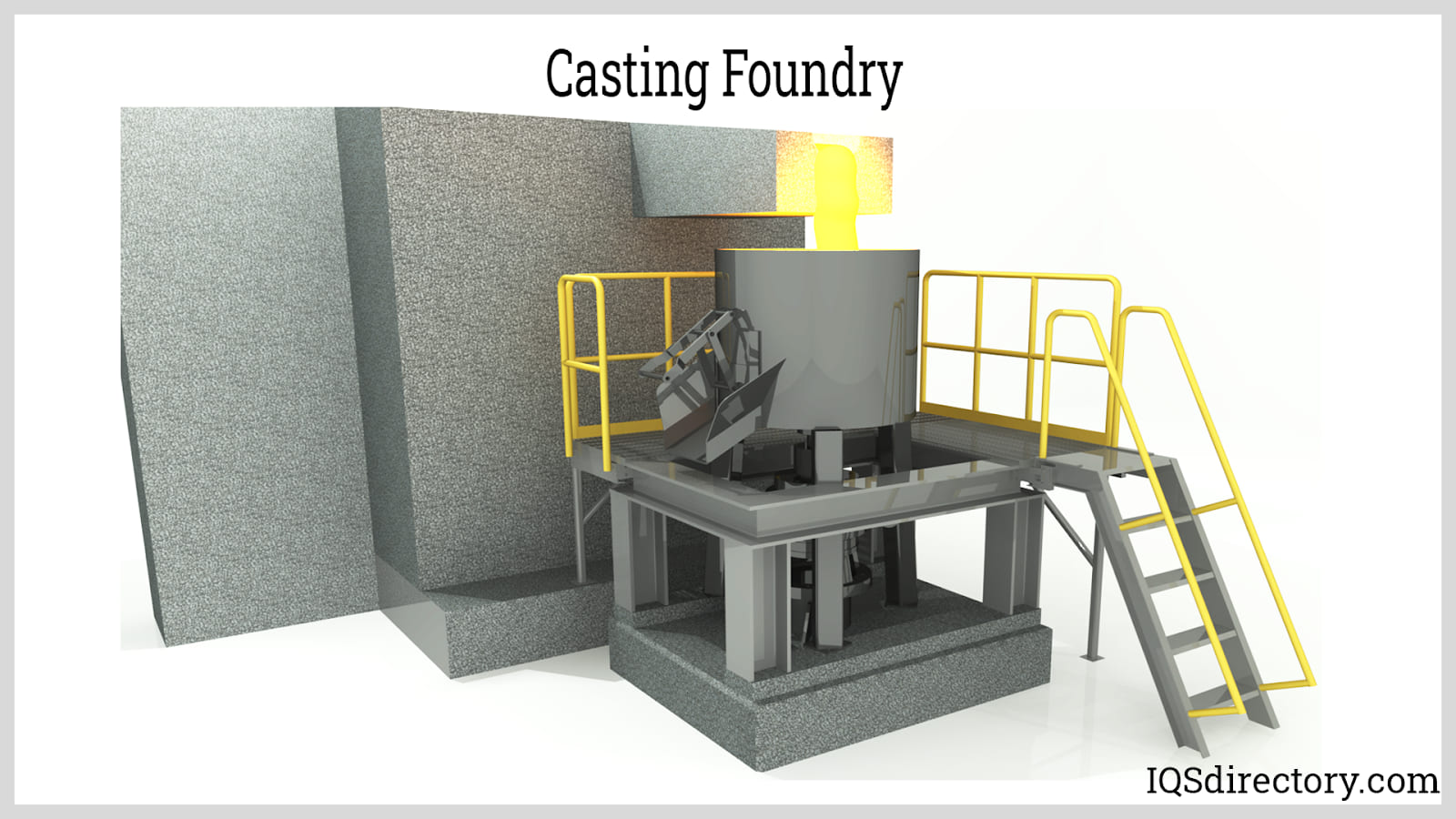
3. Melting and Casting
- The selected metal or alloy is melted in a furnace (such as induction, electric arc, cupola, or crucible furnaces) until it reaches the correct pouring temperature.
- Molten metal is ladled or injected into the prepared molds. The filled molds are allowed to cool and solidify, forming the part’s final geometry.
- Once solidified, the mold is broken or opened, and the casting is removed for further processing.
- Process control and temperature monitoring are critical for minimizing defects such as porosity, shrinkage, or cold shuts.
4. Fettling (Cleaning and Finishing)
- During fettling, excess material, such as sand, gates, risers, or flash, is removed. The casting’s surface is cleaned and made uniform using processes like shot blasting, grinding, or tumbling.
- Some castings may require heat treatment to enhance mechanical properties, relieve internal stresses, or improve microstructure at this stage.
- Additional secondary processes may include surface coating, painting, powder coating, or CNC machining for critical features.
5. Testing, Inspection, and Quality Control
- Every casting undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure it meets the required specifications, tolerances, and quality standards. This may involve visual checks, dimensional measurements, and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as X-ray, ultrasonic, or magnetic particle inspection.
- Defective castings are identified and either reworked or scrapped to maintain high performance and safety standards. Only flawless castings are dispatched from the foundry.
- Quality control may also include metallurgical analysis, tensile testing, impact testing, and traceability documentation for mission-critical components.
Types of Metal Casting Processes: Which Method Fits Your Application?
There are several metal casting techniques, each with unique advantages, limitations, and best-fit applications. Understanding the differences between these processes is critical for engineers, procurement specialists, and manufacturers seeking optimal solutions for their projects. Below, we explore the four most widely used metal casting process types for industrial and commercial manufacturing:
Sand Casting
Sand casting is the most common and cost-effective metal casting process, ideal for producing large components, low to medium production runs, and complex geometries. This method utilizes a reusable pattern and a single-use sand mold. The sand, often mixed with clay or a chemical binder, forms the mold cavity that shapes the final product.

Key benefits of sand casting:
- Low tooling and mold costs, making it ideal for prototyping and short production runs.
- Ability to produce parts in a wide range of sizes, from ounces to thousands of pounds.
- Suitable for ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including gray iron, ductile iron, steel, bronze, and aluminum alloys.
- Compatible with intricate designs and internal features using cores.
- Flexible enough for custom metal castings, discontinued parts, and legacy equipment components.
Common sand casting applications: Engine blocks, pump housings, valve bodies, machine bases, and custom industrial parts.
Who should choose sand casting? If you need large, durable metal parts or prototypes with moderate complexity, or are looking for a cost-effective solution for short or medium production runs, sand casting is likely your best match. Browse sand casting foundries or get a quote for your project.
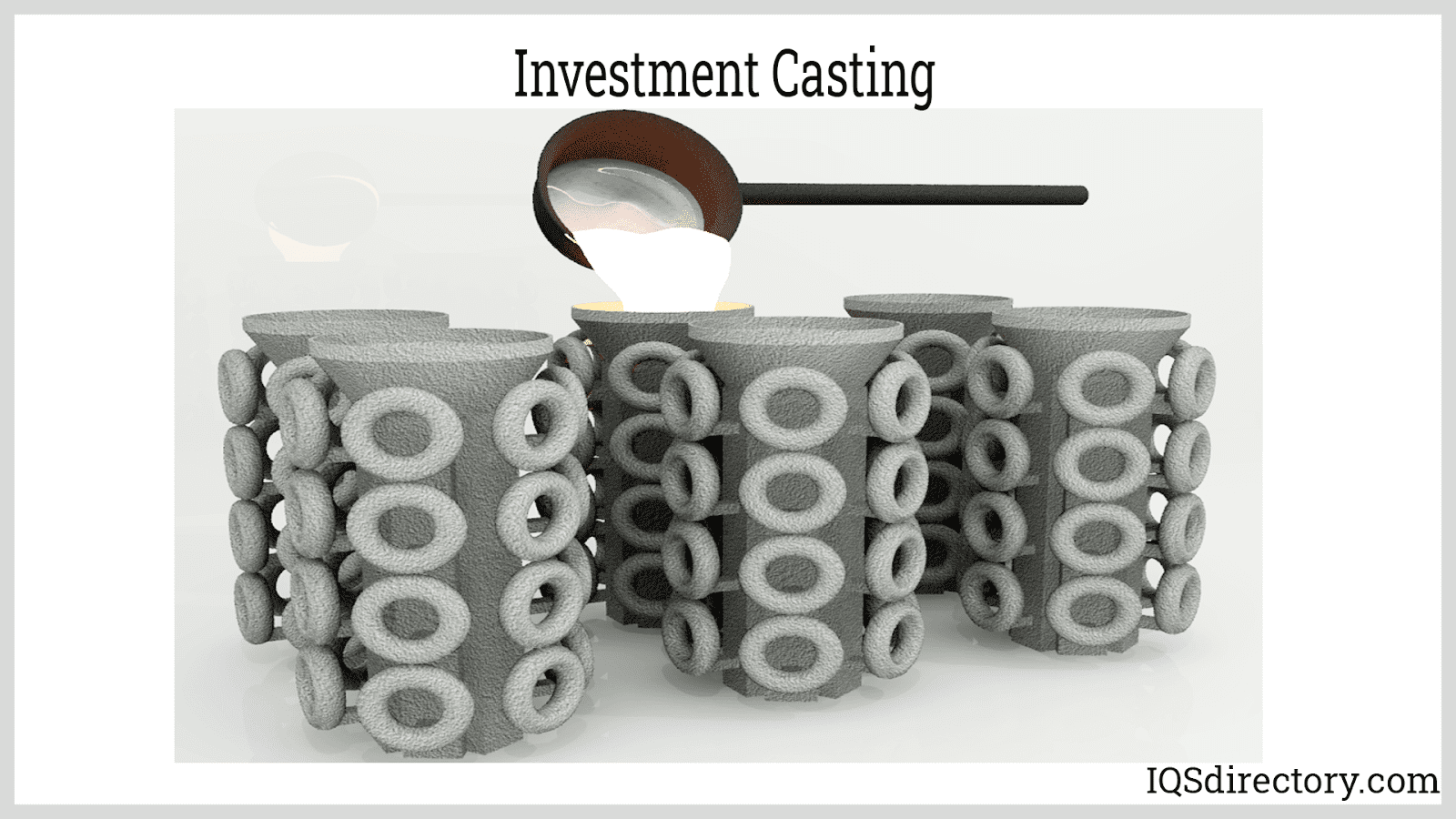
Investment Casting (Lost Wax Casting)
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, is a precision casting process used for producing intricate, high-accuracy parts with excellent surface finishes. The process involves creating a wax pattern, coating it with refractory ceramic material to form a shell, then melting out the wax and pouring metal into the cavity.
- Fabrication of a master pattern
- Creation of master dies for wax pattern production
- Preparation and assembly of wax patterns
- Application of ceramic coatings (shell building)
- Drying and hardening of ceramic layers
- Wax removal (dewaxing) and firing of the ceramic shell
- Pouring molten metal into the heated shell
- Shell removal and casting cleaning

Advantages of investment casting:
- Superior surface finish and tight dimensional tolerances
- Ability to cast intricate, thin-walled, and detailed shapes
- Minimal need for secondary machining
- Suitable for a wide variety of metals and alloys, including stainless steel, tool steel, cobalt, and nickel alloys
- Excellent for high-value, mission-critical components where quality and precision are paramount
Typical investment casting applications: Aerospace turbine blades, medical implants, high-precision gears, jewelry, firearm components, and automotive parts.
Is investment casting right for your parts? If you require detailed, complex shapes with minimal post-processing, and need to use specialty alloys or achieve repeatable high-precision results, investment casting is an ideal choice. Connect with investment casting suppliers or request a quote for your next precision project.
Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting utilizes a durable metal mold (typically steel or cast iron) that can be reused for thousands of cycles. This method is ideal for producing medium to high volumes of non-ferrous metal parts with consistent quality, close tolerances, and improved mechanical properties due to rapid solidification.
- Gravity feed permanent mold casting
- Low-pressure permanent mold casting
- Die casting
- Centrifugal casting
- Continuous casting

Benefits of permanent mold casting:
- Enhanced surface finish and dimensional accuracy compared to sand casting
- Faster production rates and lower labor costs for large batches
- Improved material properties due to faster cooling rates
- Excellent repeatability and suitability for automated production lines
- Ideal for mid-volume to high-volume manufacturing of consistent, high-quality parts
Common permanent mold casting applications: Automotive wheels, cylinder heads, gear housings, lighting fixtures, and marine hardware.
When should you use permanent mold casting? If your product requires high strength, consistent quality, and you anticipate medium to high production volumes, permanent mold casting provides an optimal balance of cost and performance. Search for permanent mold casting companies for your application.
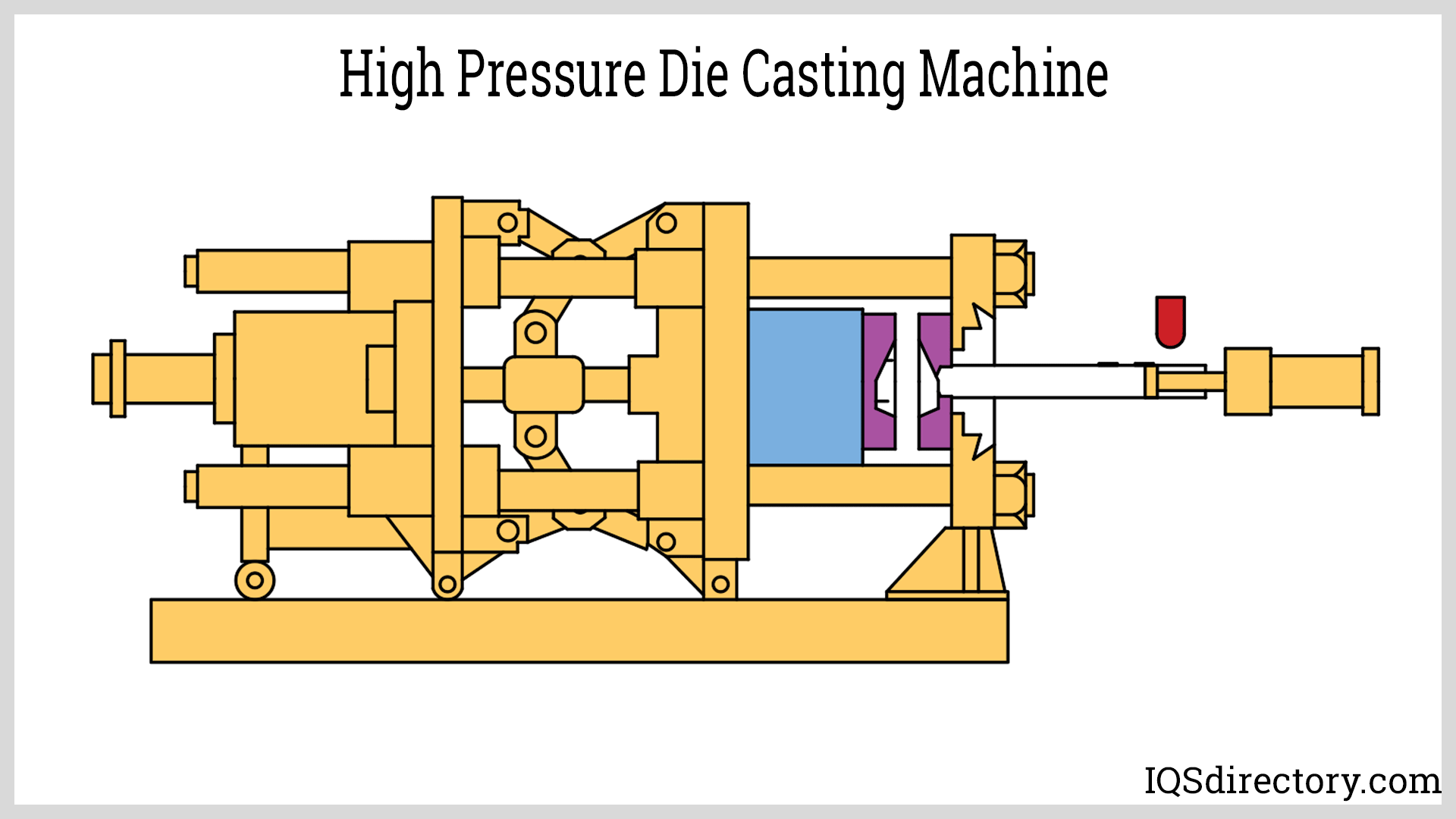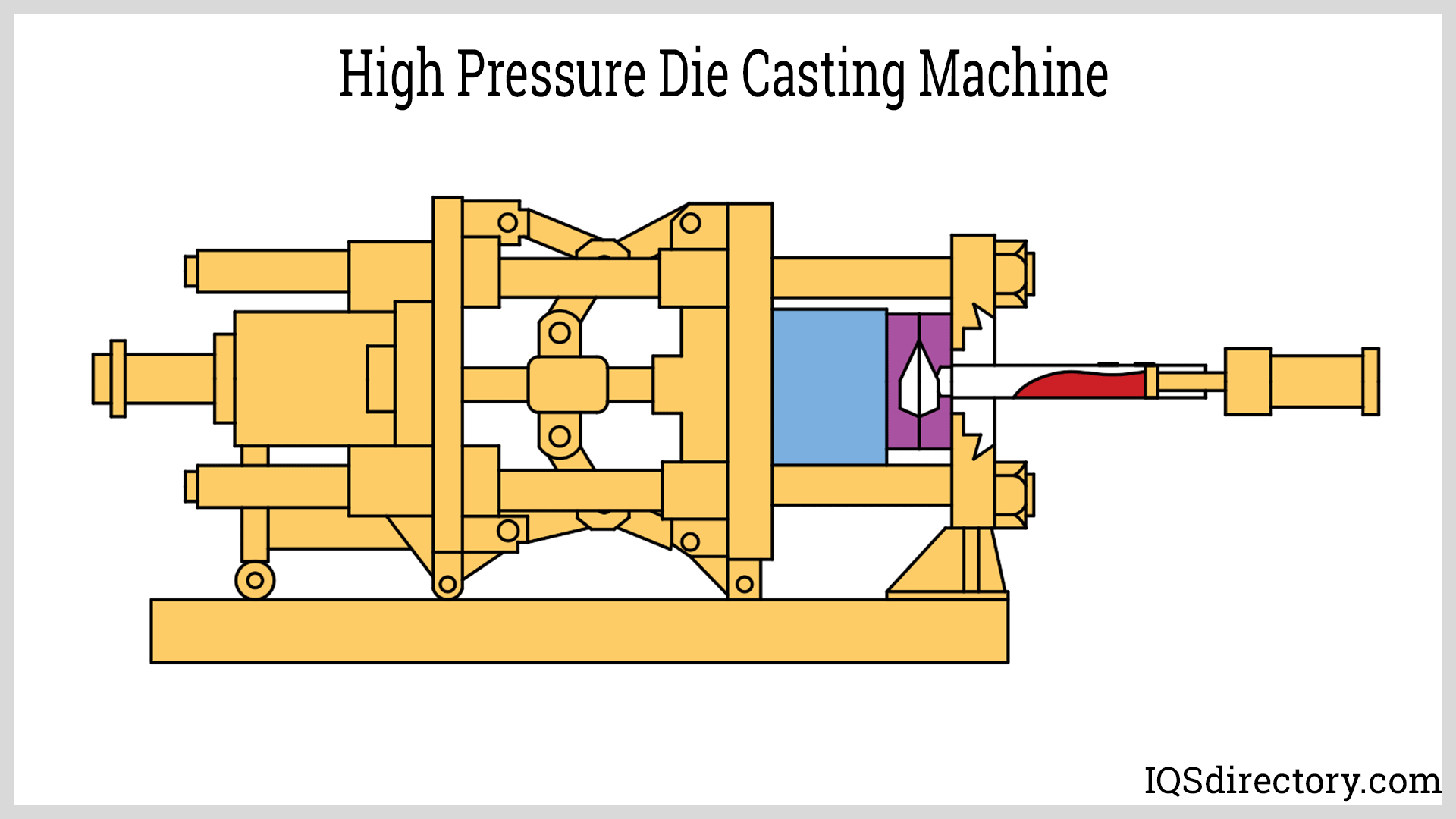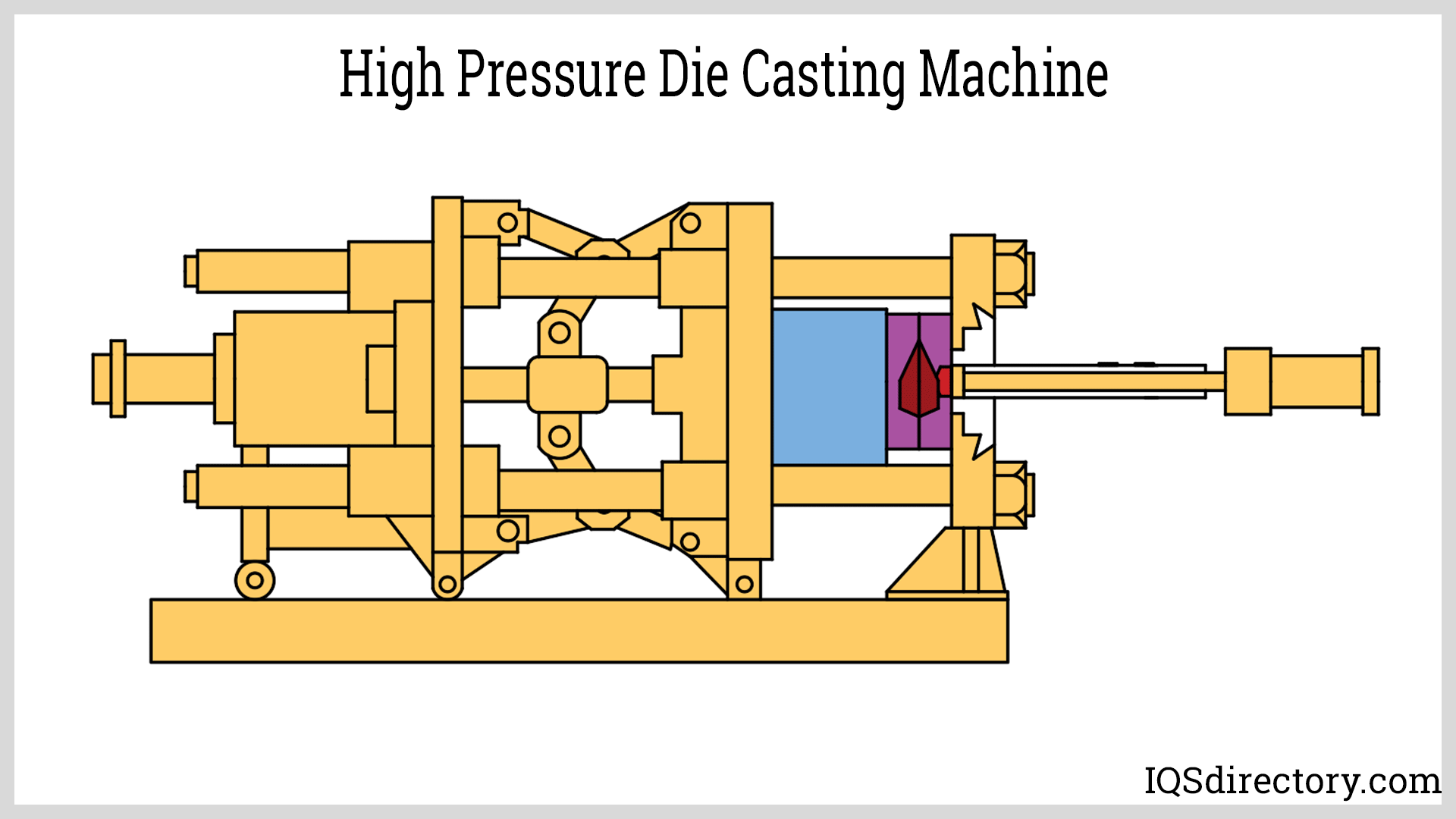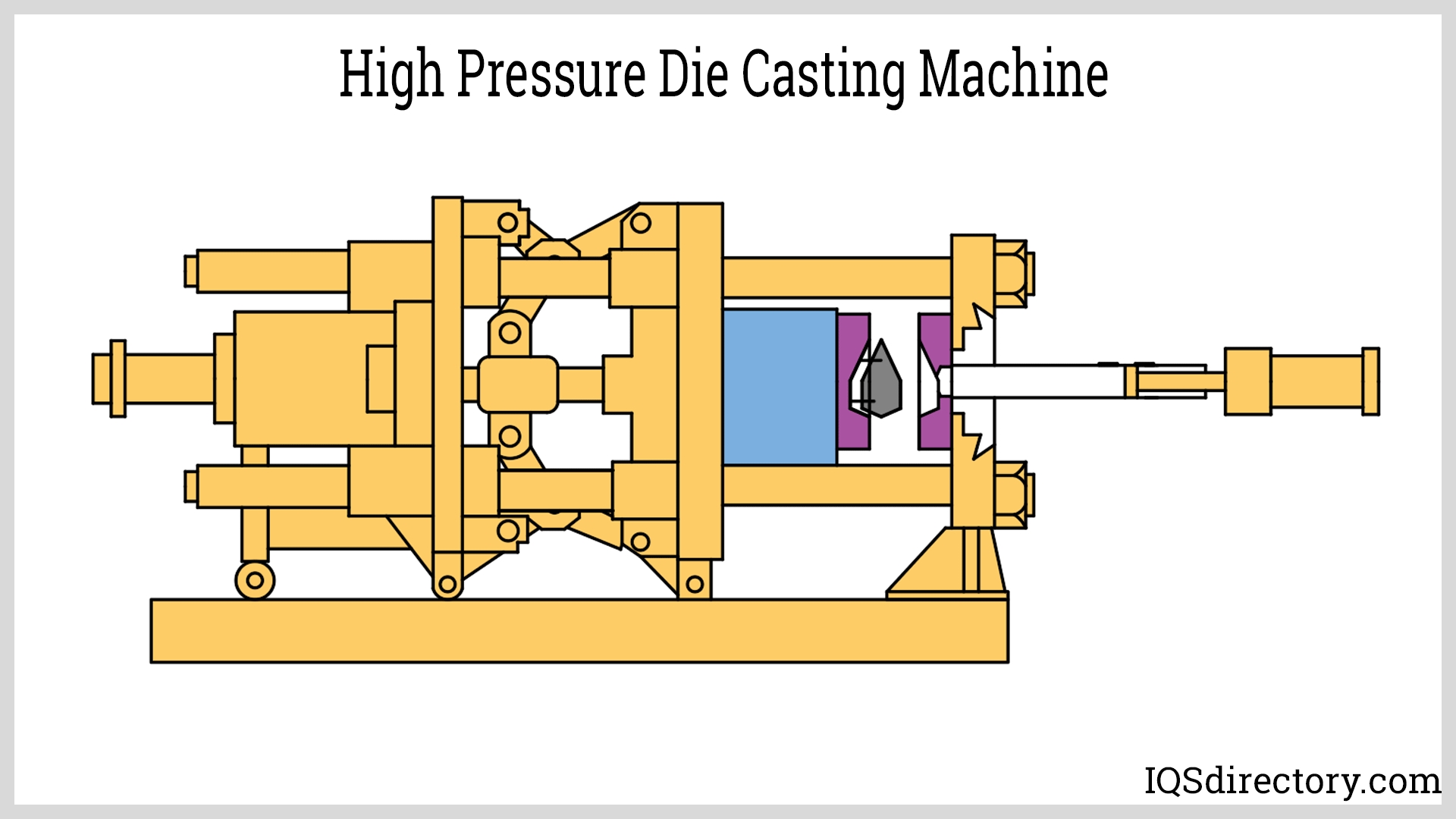
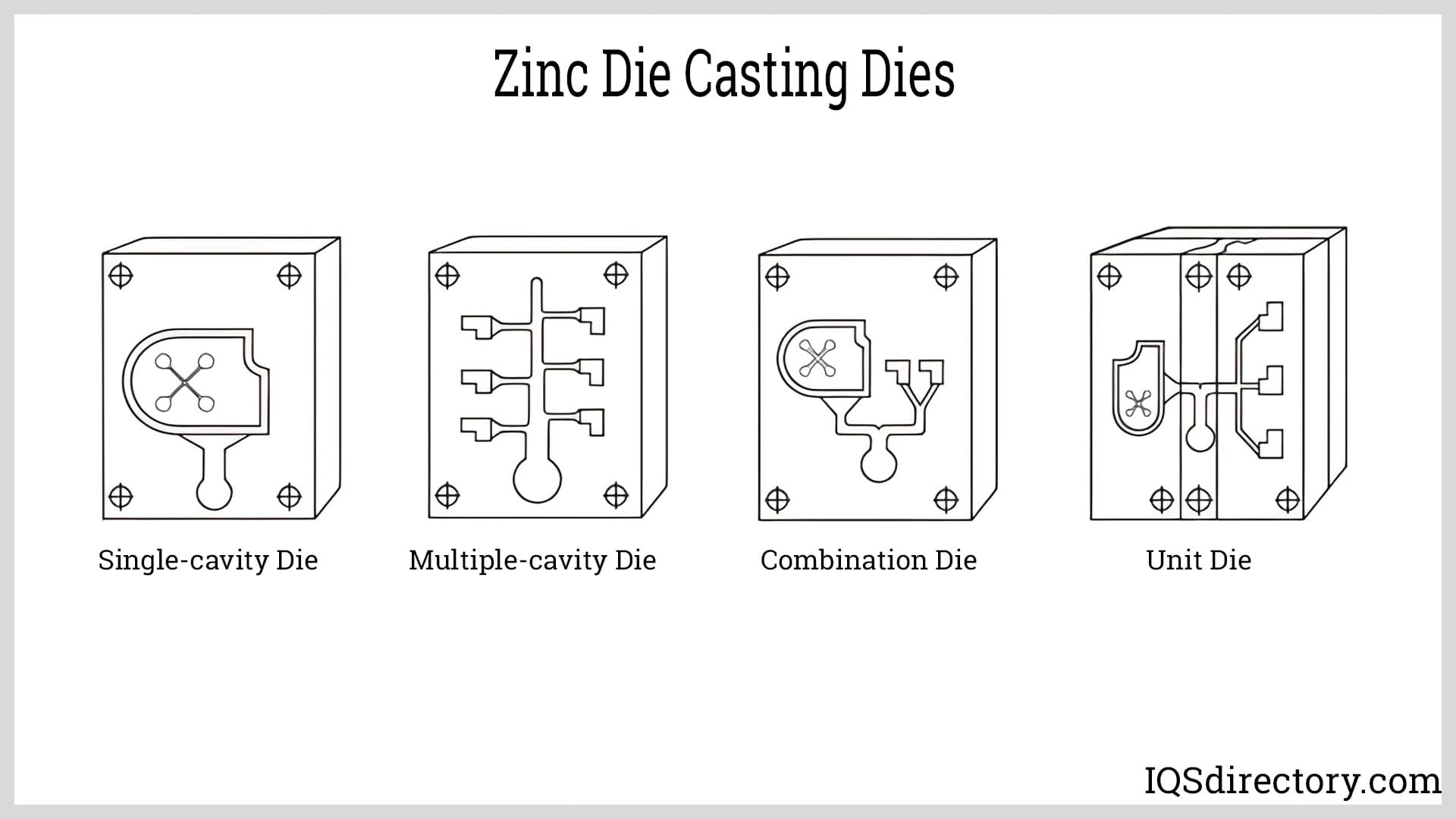
Die Casting
Die casting is a high-speed, high-volume manufacturing process in which molten metal is injected under pressure into a steel mold (die). Die casting is especially suited for producing complex, thin-walled parts from non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys.

Key characteristics of die casting:
- Exceptional dimensional accuracy and repeatability
- Excellent surface quality, often requiring little or no secondary finishing
- Rapid production cycles and high part-to-part consistency
- Suitable for manufacturing components with complex geometries, intricate detailing, and fine features
- Die casting molds (dies) are expensive to produce but cost-effective for large production volumes
- Two main types: hot-chamber die casting (for zinc, magnesium) and cold-chamber die casting (for aluminum, brass, copper alloys)
Typical die casting applications: Automotive transmission housings, electronic enclosures, appliance parts, power tool casings, and consumer electronics components.
Is die casting the best solution for your product? If you need thousands or millions of identical, high-precision, non-ferrous metal parts with excellent surface finish and minimal machining, die casting delivers speed and value. Find die casting manufacturers or start your quote today.
Comparing Metal Casting Methods: Which is Best for Your Project?
Are you wondering which metal casting process best suits your industry or application? Consider these factors when evaluating sand casting, investment casting, permanent mold casting, and die casting:
- Production Volume: Sand casting is ideal for low-to-medium runs; die casting and permanent mold casting excel in high-volume production.
- Part Complexity: Investment casting offers the highest precision for intricate designs, while sand casting is best for large, simple shapes.
- Material Selection: Sand and investment casting support a broader range of alloys; die and permanent mold casting are typically used for non-ferrous metals.
- Cost Considerations: Sand casting and investment casting have lower tooling costs; die casting offers lower per-part costs at scale.
- Surface Finish and Tolerances: Investment and die casting deliver superior finish and tighter tolerances, reducing the need for secondary machining.
- Lead Time: Sand and investment casting are faster for prototyping; die and permanent mold casting require longer setup but excel at rapid, repeatable production.
- Post-Processing Needs: Consider if your application requires additional finishing, machining, or surface coatings for optimal performance.
Still unsure? Ask yourself:
- What is my required production quantity and lead time?
- How complex is my part geometry?
- What metal or alloy best meets my part’s performance requirements?
- What is my budget for tooling and per-part costs?
For tailored recommendations, contact our metal casting consultants or use our RFQ form to get competitive bids from leading foundries.
Advantages of the Metal Casting Process
Metal casting delivers several unique advantages over other manufacturing methods, making it a preferred choice for various industries and applications.
- Lower production costs for complex or large components compared to machining or fabrication
- Ability to create single-piece castings that reduce assembly time, potential leak paths, and points of failure
- Excellent material utilization, minimizing waste and scrap
- Supports mass production and batch production with consistent quality
- Enables the use of specialty alloys engineered for corrosion resistance, high strength, or unique thermal properties
- Highly scalable, from rapid prototyping to full-scale manufacturing
- Allows for the integration of complex features such as undercuts, internal channels, and branding directly into the casting
- Offers the potential for lighter weight components through optimized design and alloy selection
Looking for more reasons to choose metal casting for your next project? Explore our in-depth resources on the benefits of metal casting and discover how it can optimize your design, supply chain, and bottom line.
Metal Casting: Industry Applications and Use Cases
Metal casting is a foundational process in a wide variety of industries. Some key sectors that rely on cast metal components include:
- Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission cases, wheels, suspension arms, brake components, turbocharger housings, intake/exhaust manifolds
- Aerospace: Turbine blades, structural supports, landing gear, control surfaces, brackets, housings
- Energy: Wind turbine hubs, hydroelectric components, oil & gas valves, nuclear containment parts, heat exchangers, electrical switchgear
- Construction & Infrastructure: Pipe fittings, manhole covers, bridge supports, architectural hardware, rail components
- Industrial Machinery: Pumps, compressors, gear housings, machine tool bases, impellers, press frames
- Consumer Goods: Appliance housings, cookware, lighting fixtures, hardware, decorative hardware
- Medical Devices: Orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, dental frameworks
- Electronics: Heat sinks, enclosures, connectors, EMI shielding components, chassis, display housings
- Marine: Propellers, hull fittings, valves, anchors, winch housings
- Rail & Heavy Transport: Bogie frames, couplers, brake shoes, wheel centers
Want to know if metal casting is right for your industry or product? Explore solutions by industry or ask a metal casting engineer for guidance.
Key Decision Factors in Selecting a Metal Casting Supplier
Choosing the right metal casting company is essential to ensuring product quality, on-time delivery, and cost-effectiveness. When evaluating potential suppliers, consider these critical factors:
- Technical Expertise: Does the foundry have experience with your specific casting process, alloy, and application?
- Quality Assurance: Are ISO certifications, process controls, and inspection capabilities in place?
- Production Capacity: Can the supplier handle your project’s volume requirements and meet deadlines?
- Engineering Support: Does the company offer design optimization, prototyping, and value-added services?
- Cost and Lead Time: Are quotes transparent, competitive, and aligned with your budget and schedule?
- Past Performance: Can the foundry provide references or case studies demonstrating successful projects?
- Supply Chain Integration: Does the supplier offer logistics, inventory management, or just-in-time delivery for your operation?
- Material Traceability: Is there documentation and traceability for metal alloys and certifications for regulatory compliance?
Ready to compare metal casting suppliers? Our comprehensive metal casting directory allows you to search by process, material, and industry. Review company profiles, explore their capabilities, and request quotes quickly using our streamlined RFQ form.
Choosing the Right Metal Casting Business
For the best results when selecting a metal casting company, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of metal casting businesses. Each company profile highlights areas of expertise, process capabilities, and equipment, along with a direct contact form for quote requests or additional information. Review each supplier’s website using our proprietary previewer to better understand their services, facilities, and quality standards. Then, use our RFQ form to contact multiple metal casting companies simultaneously, saving you time and helping you secure competitive pricing for your next project.
Need help specifying your requirements? Contact our team, to learn more about process selection, design tips, and quality control for your application.
Frequently Asked Questions About Metal Casting
- What metals can be cast? Most meltable metals—including aluminum, iron, steel, brass, bronze, magnesium, copper, and zinc alloys—can be cast using various processes.
- How do I choose between sand casting, investment casting, and die casting? Consider production volume, part size and complexity, material requirements, surface finish, and cost.
- What is the typical lead time for a custom casting? Lead times vary by process; sand and investment casting are faster for prototypes, while die casting suits high-volume production.
- Can metal castings meet tight tolerances? Yes, especially with investment and die casting, which offer high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish.
- How do I find a reliable casting supplier? Use our metal casting company directory to compare suppliers, review their certifications, and request quotes.
- What are common casting defects and how are they prevented? Porosity, shrinkage, cold shuts, and inclusions are among the most common defects. Proper mold design, temperature control, gating systems, and quality inspections minimize these issues.
- Can castings be customized for unique applications? Absolutely. Custom metal casting is frequently used for one-off prototypes, legacy parts, and highly engineered components.
Still have questions? Ask a metal casting specialist or explore our knowledge base for detailed guides, case studies, and technical articles.
Next Steps: Bringing Your Metal Casting Project to Life
Ready to start your metal casting project? Use our metal casting supplier directory to find reputable foundries, or submit a quote request for fast, competitive pricing. Our resources are designed to help manufacturers, engineers, and product developers navigate the selection, specification, and sourcing of top-tier metal casting services. Whether you’re creating a new product, replacing a legacy part, or scaling up for mass production, our expert network and comprehensive guides will support you at every stage.








 Die Castings
Die Castings Forgings
Forgings Grey Iron Castings
Grey Iron Castings Investment Castings
Investment Castings Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services